
📚 The definition of 301 and 302 redirections:ģ01 - means that the resource (page) is moved permanently to a new location. Then, and ONLY then, change the 302 redirection 301.
👌 How to avoid that? Use the 302 redirection as long as everything works as it should. If you redirect from the old domain to the new domain with the 301 redirection, browser caches it too, and prevent’s you to enter the old domain. 👉 The second example is when you changing the website domain. Browser caches the 301 redirection and redirects you to HTTPS.
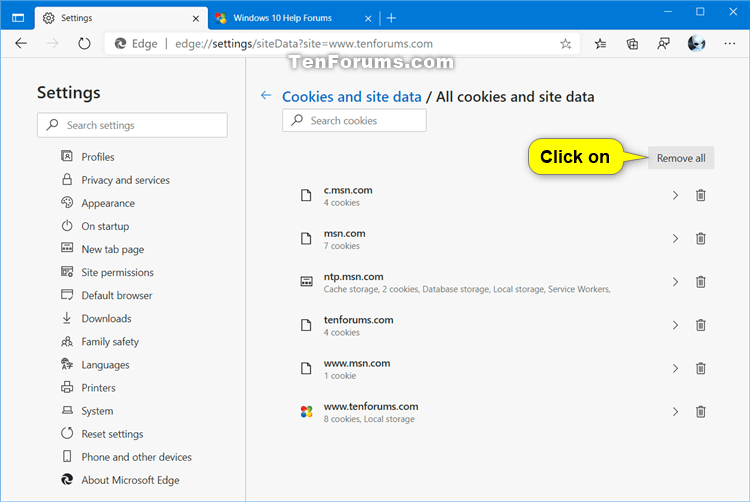
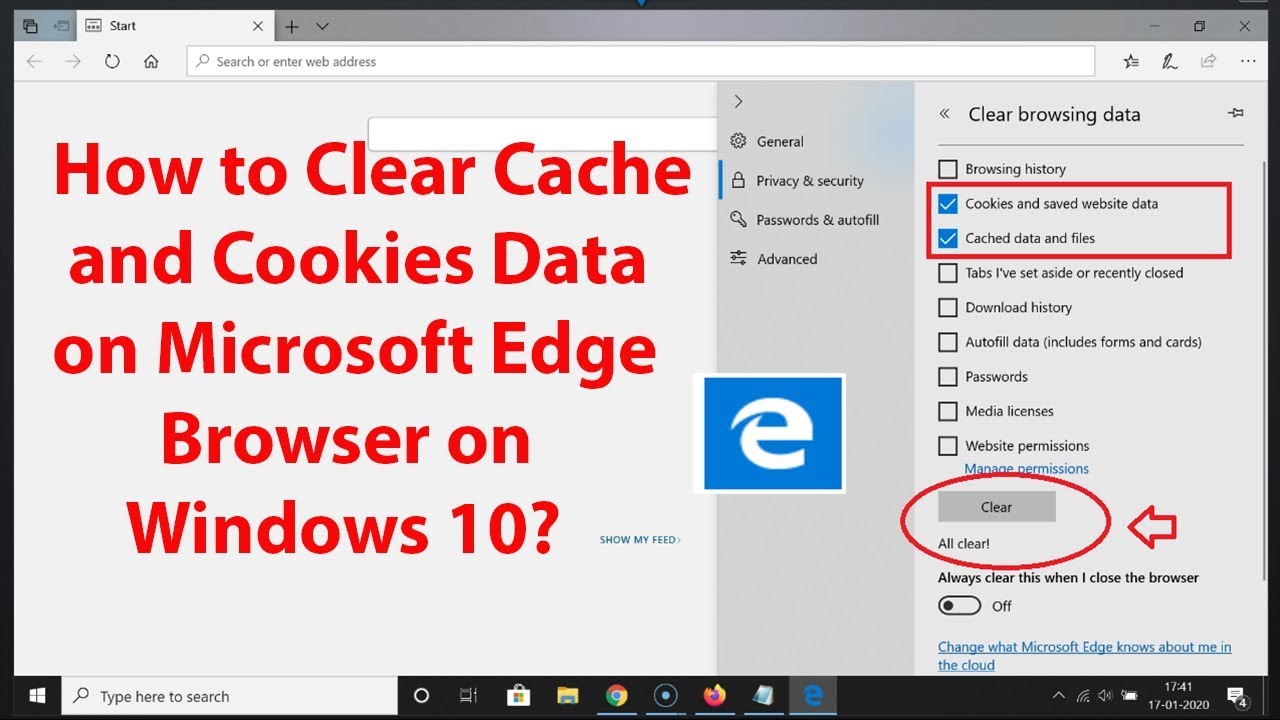
👉 For example, when you configure the SSL certificate and make the 301 redirection from HTTP to HTTPS, but something goes wrong, you don’t have the ability to enter the HTTP version again. I had facing it very often until I learn the lesson… I hope it helps you and you learn something from me, not from your mistakes 💥 In order to fix these problems, follow these simple steps.īegin by opening Google Chrome and type in this address: chrome://net-internals/#dns and press “Enter.I think many web developers and server administrators had been facing the 301 redirection cache. If you experience any DNS or host error related browsing issues, it can sometimes help to perform a DNS and Socket flush using your Google Chrome browser. Flushing your Cache through Google Chrome After you perform a flush, the next time you try to access a website, your computer will ask for all the new IP and DNS information related to that site resulting in an error free browsing experience. Just like flushing a toilet and getting rid of any old water that is stored in the tank, a DNS flush will make your computer erase any existing information regarding DNS names and IP addresses that is has stored. This is where a DNS cache flush comes in handy. Sometimes, due to continued use and accessing sites with a less than perfect web safety rating, your DNS cache may also become corrupted. When IP addresses become outdated or if a website switches to a new server, you may encounter DNS errors when you try to access them. The main purpose of this database is to make it easier for your computer to reach and access the IP addresses of websites when their servers change or if they create new servers. Your browser’s DNS Cache (Domain Name System) is essentially a small databank that stores all the IP (Internet Protocol) addresses for websites you access.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
